When a computer starts, it follows a specific sequence to determine which device it should use to load the operating system. This sequence is known as the boot order. By default, most computers are set to boot from the internal hard drive or SSD. However, there are many situations where you may need to change this order—such as installing a new operating system, booting from a USB drive, running system diagnostics, or recovering data.
Modern computers use BIOS or UEFI firmware to manage hardware initialization and boot settings. Understanding how to change the boot order in BIOS or UEFI is an essential skill for anyone who works with computers, whether you are a beginner, a technician, or a power user.
This guide explains everything you need to know, including what BIOS and UEFI are, why boot order matters, and step-by-step instructions for changing boot priority on different systems.
What Is Boot Order?
Boot order refers to the priority list of devices that a computer checks to find a bootable operating system. These devices may include:
-
Internal hard drive (HDD)
-
Solid-state drive (SSD)
-
USB flash drive
-
External hard drive
-
DVD or CD drive
-
Network boot (PXE)
The computer checks each device in order until it finds a bootable system. If the first device does not contain one, it moves to the next.
Understanding BIOS and UEFI
What Is BIOS?
BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is older firmware found in legacy computers. It initializes hardware components and loads the operating system. BIOS uses text-based menus and keyboard navigation.
What Is UEFI?
UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is the modern replacement for BIOS. It offers faster boot times, support for larger disks, mouse navigation, and better security features like Secure Boot.
Most computers manufactured after 2015 use UEFI instead of traditional BIOS.
Why You Might Need to Change Boot Order
There are several common reasons to change boot order:
-
Installing Windows or Linux from a USB drive
-
Booting from a recovery or repair disk
-
Running antivirus or diagnostic tools
-
Booting from an external drive
-
Troubleshooting system startup issues
-
Dual-booting multiple operating systems
Without adjusting the boot order, the system may ignore the external device and boot directly into the existing operating system.
Important Things to Do Before Changing Boot Order
Before accessing BIOS or UEFI, keep the following in mind:
-
Save all your open work and shut down the computer properly
-
Connect the boot device (USB, DVD, or external drive) before restarting
-
Use the correct keys to enter BIOS/UEFI
-
Avoid changing settings you don’t understand
-
Write down original settings if needed
Making incorrect changes can prevent your system from booting properly.
How to Access BIOS or UEFI Settings
Common Keys to Enter BIOS/UEFI
You need to press a specific key immediately after powering on your computer. Common keys include:
-
Delete
-
F2
-
F10
-
F12
-
Esc
The correct key depends on your computer’s manufacturer.
Accessing UEFI from Windows 10/11
If fast startup prevents you from entering BIOS manually, you can access UEFI through Windows:
-
Open Settings
-
Go to System
-
Select Recovery
-
Click Restart now under Advanced startup
-
Choose Troubleshoot
-
Select Advanced options
-
Click UEFI Firmware Settings
-
Choose Restart
Your system will boot directly into UEFI settings.
How to Change Boot Order in BIOS (Legacy Systems)
Step 1: Enter BIOS Setup
-
Restart your computer
-
Press the BIOS key repeatedly during startup
-
You will see the BIOS setup screen
Step 2: Navigate to Boot Menu
-
Use arrow keys to find the Boot, Boot Options, or Advanced BIOS Features tab
-
Press Enter to open it
Step 3: Locate Boot Priority Settings
Look for options such as:
-
Boot Device Priority
-
Boot Order
-
First Boot Device
-
Boot Sequence
Step 4: Change Boot Order
-
Highlight the desired boot device
-
Use keys like +, –, F5, or F6 to move it up or down
-
Set USB or DVD as the first boot device if required
Step 5: Save and Exit
-
Press F10 or choose Save & Exit
-
Confirm by selecting Yes
-
The computer will restart with the new boot order
How to Change Boot Order in UEFI (Modern Systems)
Step 1: Enter UEFI Firmware Settings
-
Restart your system
-
Press the UEFI access key
-
You may see a graphical interface with mouse support
Step 2: Open Boot Settings
-
Navigate to the Boot or Boot Priority section
-
Some systems place boot options under Advanced Settings
Step 3: Change Boot Priority
-
Drag and drop devices to reorder them (on supported systems)
-
Or select a device and move it using on-screen instructions
-
Set USB or external drive as the top priority if needed
Step 4: Disable Secure Boot (If Necessary)
Some bootable USBs require Secure Boot to be disabled:
-
Go to Security or Boot
-
Find Secure Boot
-
Set it to Disabled
Step 5: Save Changes and Restart
-
Click Save Changes
-
Exit UEFI
-
Your system will restart using the new boot order
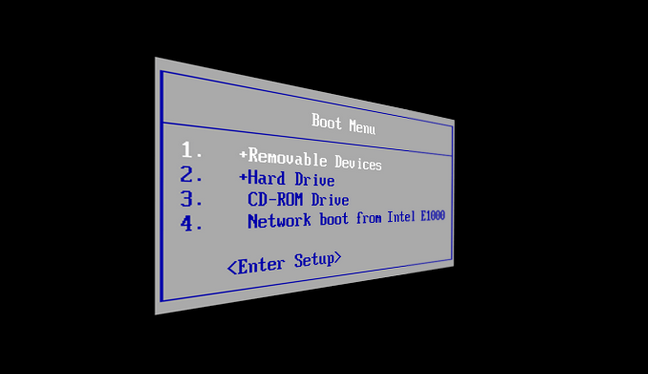
Using One-Time Boot Menu (Temporary Boot Order)
Many systems allow a one-time boot menu, which does not permanently change the boot order.
Common Boot Menu Keys
-
F12
-
F11
-
Esc
-
F8
Steps to Use Boot Menu
-
Restart your computer
-
Press the boot menu key repeatedly
-
Select the desired boot device
-
Press Enter
This is useful when you only need to boot from USB once.
Manufacturer-Specific Boot Order Instructions
Dell Computers
-
Press F12 to access boot menu
-
Press F2 to enter BIOS/UEFI
-
Go to Boot Settings
-
Reorder devices and save
HP Computers
-
Press Esc at startup
-
Press F9 for boot menu
-
Press F10 for BIOS settings
Lenovo Computers
-
Press F2 or Fn + F2
-
Some models have a Novo button
-
Navigate to Boot tab to change order
ASUS Computers
-
Press Delete or F2
-
Use Advanced Mode for boot settings
-
Drag boot devices to reorder
Common Boot Order Problems and Solutions
USB Not Showing in Boot Menu
Possible causes:
-
USB not bootable
-
USB inserted after startup
-
Secure Boot enabled
-
Legacy support disabled
Solution:
-
Recreate bootable USB
-
Enable Legacy or CSM mode
-
Disable Secure Boot if needed
System Boots to Wrong Device
Solution:
-
Double-check boot priority
-
Remove non-bootable external devices
-
Save BIOS changes properly
Boot Loop After Changing Boot Order
Solution:
-
Enter BIOS again
-
Restore default settings
-
Set internal drive as first boot device
Difference Between Legacy Boot and UEFI Boot
| Feature | Legacy BIOS | UEFI |
|---|---|---|
| Interface | Text-based | Graphical |
| Boot Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Disk Support | Up to 2TB | More than 2TB |
| Security | Basic | Secure Boot |
| Mouse Support | No | Yes |
Understanding this difference helps when configuring boot devices correctly.
Tips for Safe BIOS/UEFI Configuration
-
Only change necessary settings
-
Avoid overclocking unless experienced
-
Keep firmware updated
-
Always save changes before exiting
-
Use default settings if unsure
When Should You Reset BIOS to Default?
You may need to reset BIOS if:
-
System fails to boot
-
Wrong boot device selected
-
BIOS settings corrupted
-
Hardware changes cause errors
Most BIOS menus include a Load Default Settings option.
Final Thoughts
Changing the boot order in BIOS or UEFI is a fundamental skill that can help you install operating systems, troubleshoot startup problems, and recover data from damaged systems. While the process may look intimidating at first, following step-by-step instructions makes it safe and manageable.
Always remember to proceed carefully, make only necessary changes, and save your settings before exiting. Whether you are working with an old legacy BIOS or a modern UEFI system, understanding boot order control gives you greater flexibility and control over your computer.